1. Muscle pain

Muscle soreness may be indicative of a deficiency in collagen, an essential nutrient for optimal muscle function. If this nutrient is missing from your diet, it could be the cause.
2. Joint pain
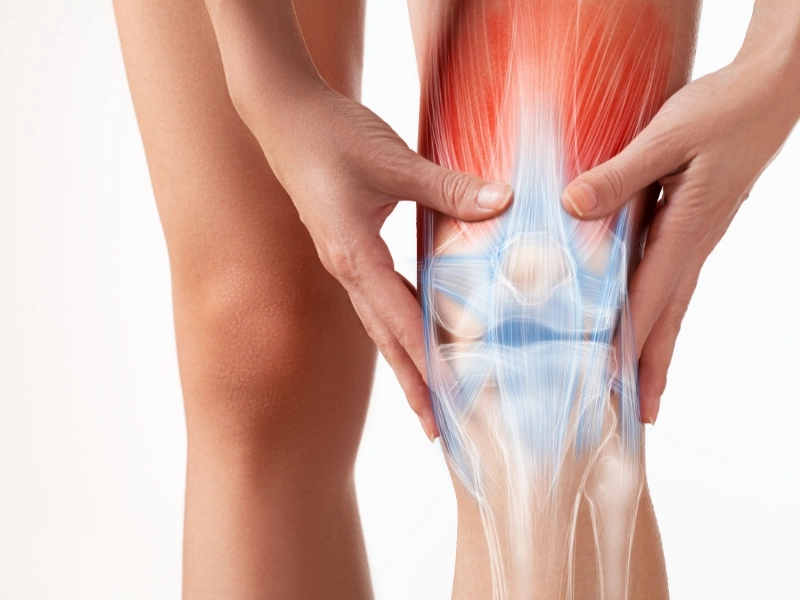
If you are experiencing joint pain and inflammation, it could be an indication that your body lacks collagen. Collagen is the protein responsible for providing flexibility in connective tissues and cartilage, so as collagen levels drop, so does flexibility in those connective tissues and cartilage. Joints need collagen to stay flexible, absorb shock and provide structural integrity. Without sufficient levels of collagen in the cartilage, it begins to deteriorate – leading to chronic joint pain. In addition to offering joint support, collagen also helps in tissue repair. Studies have shown that those who supplement with collagen report less joint pain and increased mobility.
3. Thin skin

Collagen is a protein that binds tissues and cells together. It is found in connective tissue, tendons, skin, bones and cartilage. Additionally, vitamin D helps in tissue repair, cell communication and migration, as well as the body's immune response. As we age, collagen production declines and elastin, which gives skin its youthful elasticity, is depleted.
4. Wrinkles

Lack of collagen in the body can leave skin less firm and smooth. Its elasticity and softness will also deteriorate, making it vulnerable to damage from environmental elements. Wrinkles develop when the body begins to break down collagen and elastin, two essential structural proteins. Small muscle contractions during facial expressions such as smiling or frowning can create lines on the forehead (frown lines), as well as around the eyes (crow's feet).
5. Loss of bone mass

Collagen is the protein responsible for building bones, skin, muscles, tendons and other connective tissues. Contains the amino acids glycine, proline and lysine. Bone is a living tissue that continually breaks down and rebuilds itself to maintain its strength. During childhood and adolescence, new bone forms more rapidly than old bone is broken down, creating an environment for rapid bone regrowth. By age 30, the body begins breaking down old bones more quickly than it creates new ones, leading to bone loss or osteoporosis. This may be due to genetics, lifestyle choices, or certain medical conditions such as cancer.









